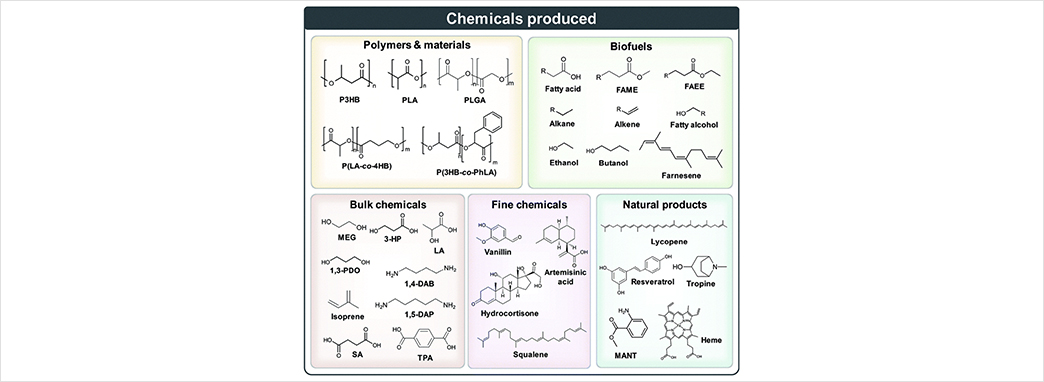
A wide range of chemicals and materials producible by systems metabolic engineering with increasing efficiencies
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee published several high-impact papers this year. In a study published in Nature Communications this year, his research team achieved the optimal production of succinic acid, an important industrial platform chemical, by using a bacterium called Mannheimia succiniciproducens [1]. In particular, the crystal structure of key enzymes important for the succinic acid production were characterized, and further engineered for the improved production. In another study, together with a research team at Technical University of Denmark, his research team published a protocol for efficient genome engineering of streptomycetes, a group of bacteria known for the production of highly valuable medicinal chemicals [2]. This protocol paper appeared in Nature Protocols this year. Besides these two studies, another two studies appeared in Nature Biotechnology [3] and Nature Chemical Biology [4], which report systematic testing of computational models and cellular compartment engineering, respectively, where Prof. Lee participated as a member of international collaborations. Several high-impact reviews have also been released this year, including those in Chemical Society Reviews [5], Advanced Materials [6] and Trends in Biotechnology [7]. Finally, Prof. Lee recently joined Executive Board of Advanced Science, a high-impact multidisciplinary journal published by Wiley-VCH.
References:
1. Ahn et al. Enhanced succinic acid production by Mannheimia employing optimal malate dehydrogenase. Nature Communications 11:1970 (2020)
2. Tong et al. CRISPR-Cas9, CRISPRi and CRISPR-BEST-mediated genetic manipulation in streptomycetes. Nature Protocols 15:2470-2502 (2020)
3. Lieven et al. MEMOTE for standardized genome-scale metabolic model testing. Nature Biotechnology 38(3):272-276 (2020)
4. Wei et al. Formation and functionalization of membraneless compartments in Escherichia coli. Nature Chemical Biology, In press.
5. Ko et al. Tools and strategies of systems metabolic engineering for the development of microbial cell factories for chemical production. Chemical Society Reviews 49:4615-4636 (2020)
6. Choi et al. Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates and non-natural polyesters. Advanced Materials 32(35):1907138 (2020)
7. Yang et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for natural product biosynthesis. Trends in Biotechnology 38(7):745-765 (2020)