Director, Advanced Battery Center
Professor, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST
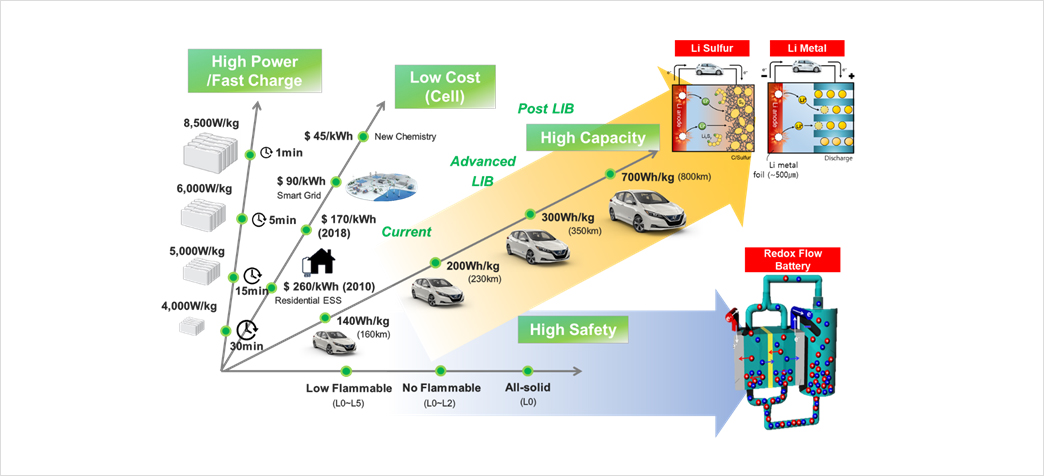
Rapid advances in secondary battery applications, including mobile electronic devices, unmanned aerial vehicles, electric vehicles and large energy storage systems, require innovative power and energy solutions for future mobility freedom and climate change issues. As the demand for energy-dense, rechargeable batteries that can power EVs and smart electronics increases, the revolution in lithium battery technology is accelerating. Among the next-generation battery candidates, lithium air, lithium-sulfur and lithium-metal batteries are attracting much attention due to their higher theoretical energy density than lithium-ion batteries. Despite the recent noteworthy development of these cells, there is still a major challenge in addressing low safety and low cycle stability issues.
On the other hand, renewable energy is regarded as one of the important means of providing energy with sustainability. With increasing energy consumption and limited fossil fuels, it is considered by many an inevitable choice. However, for efficient implementation of renewable energies including solar and wind energy in electric grid applications, an energy storage system (ESS), which provides storage of the electric energy from renewable sources and its on-demand release, is required. An ESS should be energy-efficient, safe, reliable, and cost-effective. In this regard, redox flow batteries (RFBs) have gained increasing attention for ESS applications. However, current commercially available redox flow batteries such as vanadium and Zn-Br redox flow batteries do not fully address the cost and reliability issues.
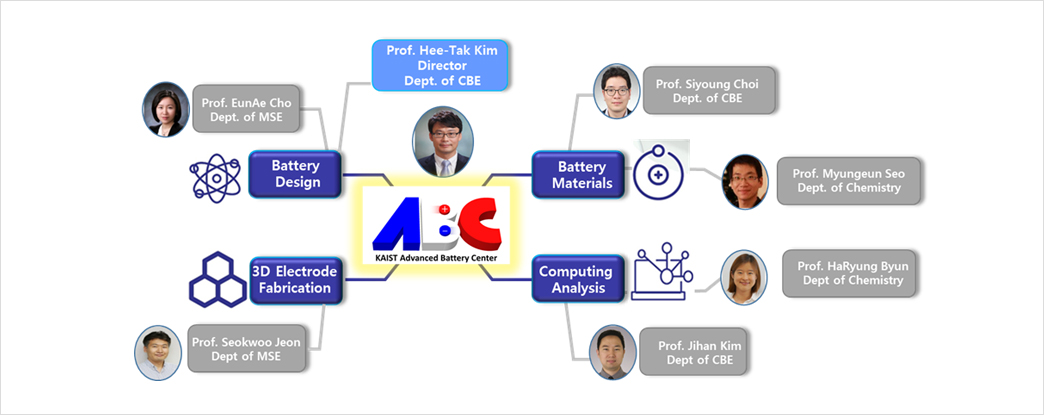
KAIST's Advanced Battery Center (ABC), a division of KAIST's NanoCentury Laboratory, was founded in 2017 to develop innovative next-generation batteries with an ambitious vision of becoming the global leader in the area of next generation battery technologies. Seven professors from Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Materials Science and Engineering, and Chemistry joined ABC. ABC currently develops lithium air, lithium sulfur and lithium metal batteries that revolutionize the cruise range of electric vehicles and unmanned aerial vehicles. Another ambitious attempt at ABC is the development of a new redox flow battery for energy storage system that can address the cost and reliability issues of current redox flow batteries. To achieve these goals, ABC is leveraging KAIST's diverse technologies (battery design, materials engineering, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytical technologies) to achieve innovation.
ABC has recently released highly important technologies in the field of next-generation batteries, including;
[Lithium oxygen battery] Nanostructuring one-dimensional and amorphous lithium peroxide for high round-trip efficiency in lithium-oxygen batteries, Nature Communications, 9, 680 (2018)
[Redox flow battery] Ion-selective graphene oxide framework for the enhanced durability of a hydrocarbon membrane in vanadium redox flow batteries, Nano Lett. 18, 3962 (2018)
[Lithium sulfur battery] An ultra-high capacity graphite/Li2S battery with holey Li2S nanoarchitectures, Advanced Science, 5, 1800139 (2018)